About small values with huge influence - Sum Of Squares - part 1
Often, the small things make the biggest difference in life. Sometimes these things we do not recognize at first as big but as soon as we draw our attention to them, they become more important.
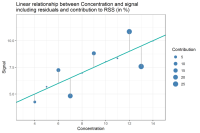
In analytical method validation, one of these small things is the so-called sum of squares or residual sum of squares (RSS). The (residual) sum of squares you will often find as a number in validation reports that, at first sight, might be of no interest at all. That is why, in this article, we will explain in more detail what this number actually means and why it is of importance. We will discuss its meaning and its importance, as well as the pros and cons and what can be done to avoid statistical pitfalls when using the RSS.